|
Dialogic SS7 Solutions Overview
SS7 is the signaling system that forms
the backbone of the international telecommunications
network. In terms of CT applications, SS7 offers a
number of advantages over conventional in-band and
common-channel signaling methods. By SS7 enabling
CT applications, application developers can realize
a number of advantages :
- an expanded customer base by network
enabling existing CT applications and making them
available to network service providers.
- improve performance from a given
application platform by taking advantage of SS7's
fast call setup. This translates to less equipment
required in the central office as well as lower
trunking costs.
- access to the Intelligent Network(IN)
by utilizing SS7's transaction services
Dialogic makes SS7 solutions available
through a partnership with DataKinetics, a worldwide
leader in SS7 connectivity. These products are sold
and supported by Dialogic.
What is SS7?
The SS7 signaling system is a packet-switch
data network that forms the backbone of the international
telecommunications network. SS7 plays an important
role in both wireline and wireless network. For example,
as the basis for GSM and IS-41 networks, SS7 allows
wireless users capabilities such as automatic roaming
that are transparent to the user.
SS7 provides two basic types of
services:
| Call
Control |
SS7 provides
fast and reliable common channel or "out-of-band"
signaling for call control. At the heart of the
SS7 call control function is a network of ultra-reliable
packet switches called Signal Transfer Points.
|
| Intelligent
Network (IN) |
The SS7
network enables the implementation of IN/Advanced
Intelligent Network (AIN) services. SS7 messages
traverse STPs and enlist the use of System Control
Points (SCP), Service Switching Points (SSP),
and Intelligent Peripherals (IP) to deliver these
services to the user. |
The SS7 network is accessed through
a set of protocols. Through DataKinetics' implementation
of the protocols, existing enterprise-based applications
can be migrated to the public network domain.
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
- Complete family of SS7 products ranging
from board to server level that easily scale from
64 ports to over 16,000 ports.
- Commom hardware architecture across
the product line offers scalable solutions from
64 to 16,384 Channel Identification Code (CIC).
- Modular, common API across the product
line means faster application development and greater
flexibility.
- Customer extensible software allows
you to design your own variants based on the needs
of the network.
- Reliable, load-sharing implementations
provide the high degree of availability that telephony
company or public network applications demand.
- E-1, T-1 or V.35 interfaces.
- Support for MTP, ISUP/TUP, SCCP,
and TCAP — including many international variants
- cPCI solutions available.
- Support for IN protocols including
GSM-MAP, IS-41, and INAP.
- Open interfaces at all levels -MTP3,
ISUP, TUP, SCCP, TCAP; offering your the ability
to customize your solutions.
- ITU, ANSI, and ETSI standards compliance.
Multiple country variants supported and Worlwide
deployment.
APPLICATIONS
The SS7 product family offers a modular
open architecture to build functional, reliable, cost-effective
public network applications and services. In addition,
the SS7 platform enables building Intelligent Network
platforms including Service Control Points (SCP),
Intelligent Peripherals (IP), Service Nodes (SN),
Service Switching Points (SSP), Mobile Switching Centers
(MSC), and Signal Transfer Points (STP). These platforms
can be used in both wireless and wireline networks.
Common applications include :
- Prepaid phone
- Prepaid calling card
- Personal productivity and personal
assistant applications
- Follow-me / One-number services
- Voice mail and Unified Messaging
- Voice-Activated Dialing
- Short Messaging Services (SMS)
- Network call center
- SS7-IP gateway
- Least-cost routing / Telecom resale
- Local number portability
- 800 / Freephone
- Calling name
- Virtual private network
- International callback
- IS-41 and GSM-MAP home location register
The SS7 Protocol Architecture
SS7 is a layered software architecture
that consists of message transfer and user parts.
The diagram above illustrates the SS7 protocol architecture
(items in gray are part of the DataKinetics software
offering).
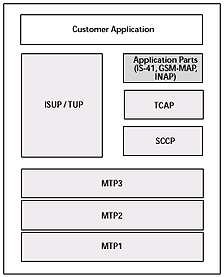
Message Transfer Part
MTP1-3 (transport): Provides the physical,
link, and network layer functions. The overall purpose
of MTP is to transport information from the upper
layers (including the user parts and SS7 applications)
across the SS7 network.
User Parts
ISUP/TUP
(call control): Provides standards-based and network-specific
call control services for wireless and wireline PSTN
networks.
SCCP
(Signal Connection Control Part): Provides address
resolution services (i.e., global title) for locating
services within the network. SCCP is available in
two versions: connectionless only and connection-oriented
plus connectionless.
TCAP
(Transaction Capabilities Application Part) (transaction
services): Used for transporting transaction-oriented
data across the SS7 network. TCAP implements standard
Remote Operation Service Invoke (ROSE) services for
applications such as GSM-MAP and IS-41. These "applications"
provide IN services such as Home Location Register
or Short Message Service.
GSM-MAP, IS-41,
and INAP: Transaction-based services that allow
development of applications such as Short Message
Service, access to HLR/VLR (for wireless networks),
and other IN applications.
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
The following terms will help you understand
SS7.
Links
Signaling data links are used to connect SS7 signaling
points. In most countries, these links are 56/64 Kb/s
data facilities. The physical interface to an intelligent
peripheral is either a T-1/E-1 interface or a V.35
connection.
Linksets
Links are grouped into linksets. All links in a linkset
must connect to a single point code. Up to 16 links
can be assigned to a single linkset.
Point Codes
Point codes define the address of SS7 network nodes.
Each switch, SCP, STP, and IP has a unique point code
in the SS7 network. In some respects, point codes
are analogous to IP addresses defined by the Internet
Protocol.
CIC
The circuit identification code (CIC) refers to a
single port or time slot on a T-1 or E-1 interface.
The combination of the point code and the CIC defines
a unique point in the network, like an Internet Protocol
IP address.
|
Products
|
Description |
|
PC-CS6
|
|
|
|
- Intelligent SS7 signaling
board
- Maximum of 3 SS7 links (1-2
ISUP links typical)
- MTP layers 1 and 2
- Single or dual network
interface options:
- E1(75ohm, 120 ohm)
- T1
- V.35
- Typically engineered for 25call/sec
- 256 or 1024 CICs options.
- Support RJ-45, BNC, D-type.
- Support slot ISA form factor
and SCbus.
- Software Support :Win 2000,
Linux.
|
|
DSC131
|
|
|
|
DSC-131SIU
- Standalone unit supports
- Single or dual network
interface options:
- E1(75ohm, 120 ohm), T1,
V.11
- Same PCCS6 API over TCP/IP
- Typically engineered for >
25call/sec
- One or two dual PCCS6
boards
- maximum of 6 SS7 links
- Up to 4096 ISUP voice ports
in 4 linksets standalone unit
- Support RJ-45, BNC, D-type.
- Same API as card
- Physical Dimensions : short
19" rack mount
- Software Support :Win 2000,
Linux.
|
|
DSC231
|
|
|
|
DSC-231SIU
- Standalone unit supports
- Single or dual network
interface options:
- E1(75ohm, 120 ohm),T1,
V.11
- Targeted to large link groups
- Same PCCS6 API over TCP/IP
- Typically engineered for 25-75+call/sec
- Greater Density
- Up to 10 PCCS6 boards/32
links
- Up to 16,384 ISUP voice
ports in 8 linksets standalone unit
- Support RJ-45, BNC, D-type.
- Same API as card
- Physical Dimensions : Std.
19" rack mount
- Software Support :Win 2000,
Linux.
|
*Preliminary Information
|